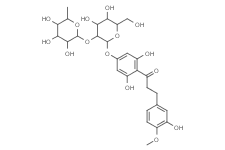
Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone
CAS No. 20702-77-6
Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone( Neohesperidin DC | NHDC )
Catalog No. M18224 CAS No. 20702-77-6
Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone(NHDC) is an artificial sweetener derived from citrus.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 38 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 52 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | 67 | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNeohesperidin Dihydrochalcone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNeohesperidin dihydrochalcone(NHDC) is an artificial sweetener derived from citrus.
-
DescriptionNeohesperidin dihydrochalcone(NHDC) is an artificial sweetener derived from citrus.(In Vitro):Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone shows remarkable radical scavenging activity against stable radical and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in concentration dependent manner. Especially, neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is the most potent inhibitor of H2O2 and HOCl. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone shows HOCl scavenging activity of 93.5% and H2O2 scavenging property of 73.5%. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone shows extensive inhibitory effect especially on non-radical ROS H2O2 and HOCl with IC50 values of 205.1, 25.5 μM. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is found to be an activator of porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase (PPA) with an IC50 of 389 μM.(In Vivo):Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone administration results in significant reduction in activities of two useful markers of liver damage, AST and ALT. The relative levels of NF-κB, IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α protein in the liver of PQ-treated mice are inhibited by neohesperidin dihydrochalcone. The embryotoxicity/teratogenicity of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is examined in Wistar Crl:(WI)WU BR rats. No adverse effects are observed at neohesperidin dihydrochalcone levels of up to 5% of the diet, the highest dose level tested, at which the rats consumed about 3.3 g/kg body weight/day.
-
In VitroNeohesperidin dihydrochalcone shows remarkable radical scavenging activity against stable radical and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in concentration dependent manner. Especially, neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is the most potent inhibitor of H2O2 and HOCl. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone shows HOCl scavenging activity of 93.5% and H2O2 scavenging property of 73.5%. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone shows extensive inhibitory effect especially on non-radical ROS H2O2 and HOCl with IC50 values of 205.1, 25.5 μM. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is found to be an activator of porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase (PPA) with an IC50 of 389 μM.
-
In VivoNeohesperidin dihydrochalcone administration results in significant reduction in activities of two useful markers of liver damage, AST and ALT. The relative levels of NF-κB, IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α protein in the liver of PQ-treated mice are inhibited by neohesperidin dihydrochalcone. The embryotoxicity/teratogenicity of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is examined in Wistar Crl:(WI)WU BR rats. No adverse effects are observed at neohesperidin dihydrochalcone levels of up to 5% of the diet, the highest dose level tested, at which the rats consumed about 3.3 g/kg body weight/day.
-
SynonymsNeohesperidin DC | NHDC
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number20702-77-6
-
Formula Weight612.58
-
Molecular FormulaC28H36O15
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 31 mg/mL; 50.61 mM
-
SMILESC[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O1)O[C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O[C@H]1Oc1cc(c(c(c1)O)C(=O)CCc1cc(c(cc1)OC)O)O)CO)O)O)O)O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Kroeze JH, Chem Senses, 2000, 25(5), 555-559.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Nonanal
Nonanal is a growth factor for wood-rotting fungi. Nonanal is a potential attractant for the pine shoot beetle.
-
CRCD2
1H-Benzimidazole-6-carboxamide, N-[3-(aminocarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thien-2-yl]- may have antitumor activity.
-
4-Fluoroanisole
Intermediates of medicine, pesticide, liquid crystal materials.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


